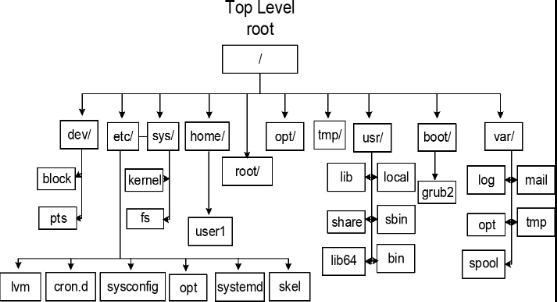
| / |
The root directory |
| /bin |
Binaries |
| /boot |
Linux Kernel, initial RAM disk image, boot loader |
| /dev |
This is a special directory that contains device nodes |
| /etc |
System-wide config files and init scripts for services |
| /etc/crontab |
|
| /etc/fstab |
File system table, lists devices mounted at boot time |
| /etc/passwd |
Where user accounts are defined |
| /etc/group |
Where user groups are defined |
| /etc/shadow |
User’s passwords |
| /home |
User directories |
| /lib |
Shared libary files used by core system programs |
| /lost+found |
Used in case of a partial recovery from a file system corruption event |
| /media |
Mount points for removalbe media such as USB, CD-ROMs, additional drives |
| /mnt |
On older Linux systems /mnt is for manually mounted removable devices |
| /opt |
Optional software |
| /proc |
Virtual file system maintained by the Linux kernel |
| /root |
Home directory for root |
| /sbin |
System binaries |
| /tmp |
Temporary files created by programs |
| /usr |
All programs and support files used by regular users |
| /usr/bin |
Executables installed by Linux Distro |
| /usr/lib |
Shared libraries for programs in /usr/bin |
| /usr/local |
Executables not from Linux Distro, usually sysadmin installed |
| /usr/sbin |
More system administration programs |
| /usr/share |
All data shared by programs in /usr/bin |
| /usr/share/doc |
Documentation for packages installed on system |
| /var |
Where changing data such as databases, spool files, mail, etc |
| /var/log |
System log files |
| /var/log/messages |
|
| /var/log/syslog |
|